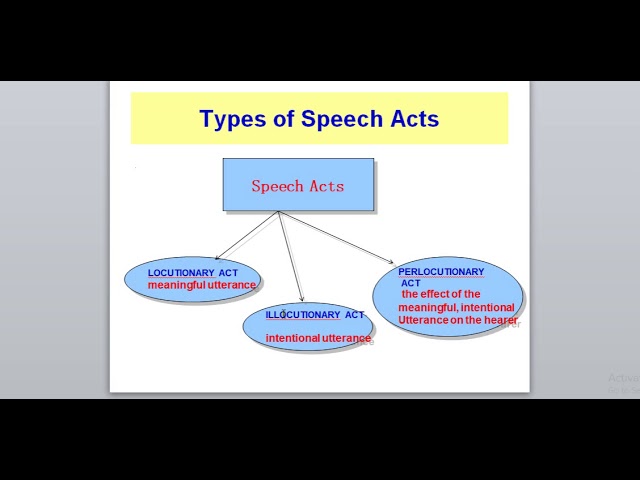
What are the Principles of Health Communication?
The principles of health communication are guidelines that promote effective communication and engagement in health-related topics. They involve creating clear and concise messages, tailoring communication to the needs of the audience, using credible sources, and fostering trust and transparency.
Health communication principles ensure that information is accurately conveyed, understood, and utilized to promote health and well-being. With these principles in place, individuals can make informed decisions, adopt healthy behaviors, and actively participate in managing their own health. Effective health communication is essential for healthcare providers, researchers, policymakers, and public health professionals to deliver and receive accurate information, ultimately improving health outcomes for individuals and communities.
Importance Of Effective Communication In Healthcare
Effective communication plays a crucial role in healthcare as it has a direct impact on patient outcomes, safety, and overall satisfaction. Without clear and efficient communication, healthcare providers may fail to understand their patients’ needs and concerns, resulting in inadequate care and negative patient experiences. In contrast, when communication is prioritized, patient-provider relationships are strengthened, patient safety is ensured, and positive health outcomes become more achievable.
Enhancing patient-provider relationships
Clear and effective communication is essential for building strong patient-provider relationships. When healthcare professionals actively listen to their patients and address their concerns, it fosters trust and a sense of partnership. Patients feel valued when their healthcare providers take the time to explain medical conditions, treatments, and procedures in a way that is easy to understand. This improved communication fosters stronger connections between patients and providers, leading to better collaboration, shared decision-making, and ultimately, improved health outcomes.
Ensuring patient safety and satisfaction
Effective communication is vital for ensuring patient safety and satisfaction. In a healthcare setting, accurate and timely exchange of information between providers and patients can prevent medication errors, misdiagnosis, and other adverse events. For example, when patients are consistently informed about their treatment plans, including medication instructions and potential side effects, they are more likely to adhere to the prescribed regimen. Consequently, patient outcomes improve, and the risk of complications decreases. Additionally, when patients feel heard and understood, their satisfaction levels increase, leading to a positive overall healthcare experience.
Fostering positive health outcomes
Efficient communication contributes to positive health outcomes by enabling healthcare providers to accurately assess and address patients’ needs. When patients are encouraged to openly discuss their symptoms, concerns, and expectations, providers can gain a comprehensive understanding of their health status. This enhances the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment plans, allowing for tailored interventions that improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, effective communication helps patients understand and manage their health conditions, empowering them to actively participate in their own care. The combination of patient-centered communication and active patient engagement leads to better health outcomes, including improved quality of life, reduced hospital readmissions, and increased patient satisfaction.

Credit: www.who.int
Principle 1: Clear And Concise Messaging
When it comes to health communication, one of the most crucial principles is to ensure that messages are clear and concise. This means using language that is easy to understand, avoiding complex terminology and medical jargon, and keeping the message simple and focused. Providing information in a clear and concise manner helps to ensure that it can be easily understood and absorbed by the target audience.
Using plain language for easy understanding
One of the key ways to achieve clear and concise messaging in health communication is by using plain language. Plain language is a style of writing that aims to communicate information in a way that is clear and easy to understand for the average reader. It involves using simple words, short sentences, and avoiding unnecessary jargon or technical terms.
By using plain language, health communicators can effectively convey their message, ensuring that it is understood by a wide range of audiences. This is particularly important when communicating health information, as it is crucial that the information is accessible to everyone, regardless of their level of health literacy.
Avoiding medical jargon and complex terminology
In addition to using plain language, it is important to avoid medical jargon and complex terminology when communicating health information. Medical jargon can be confusing for the average person, and using it can hinder their understanding of the message being conveyed.
Instead, health communicators should use simple and familiar terms that are easily understood by their target audience. By avoiding complex terminology, they can ensure that the information is accessible and easily digestible, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Keeping messages simple and focused
Finally, another important aspect of clear and concise messaging in health communication is to keep messages simple and focused. This means avoiding unnecessary information and staying on topic. By doing so, health communicators can ensure that their message remains clear and easy to follow.
To keep messages simple and focused, it can be helpful to break down complex information into smaller, more manageable pieces. This can be done through the use of bullet points or lists, tables, or by breaking up the information into smaller paragraphs.
Furthermore, health communicators should strive to keep their messages concise. By being concise, they can avoid overwhelming their audience with an excessive amount of information, increasing the chances that the message will be understood and retained.
Principle 2: Cultural Sensitivity And Diversity
One of the fundamental principles of health communication is cultural sensitivity and diversity. This principle recognizes the importance of understanding and respecting the cultural differences that exist among individuals and communities. Effective health communication requires tailoring messages and interventions to meet the diverse needs of various cultural groups, promoting inclusivity, and avoiding stereotypes.
Recognizing and Respecting Cultural Differences
In order to effectively communicate health information, it’s essential to recognize and respect the cultural differences that exist among diverse populations. Each culture brings its own unique beliefs, values, and practices related to health and wellness. By acknowledging and respecting these differences, health communicators can build trust and rapport with individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
Tailoring Communication to Meet Diverse Needs
To ensure that health information reaches and resonates with diverse populations, it’s crucial to tailor communication strategies according to their specific needs. This involves considering factors such as language barriers, literacy levels, and cultural preferences. Health messages should be communicated in a way that is accessible and understandable to individuals of varying backgrounds and abilities.
Promoting Inclusivity and Avoiding Stereotypes
Another important aspect of cultural sensitivity and diversity in health communication is promoting inclusivity and avoiding stereotypes. Inclusive communication means ensuring that messages are designed to reach and resonate with all individuals, regardless of their cultural background. It’s essential to avoid using stereotypes or perpetuating cultural biases, as this can undermine the effectiveness of health communication efforts.
To effectively promote inclusivity, health communicators should strive to represent diverse cultural perspectives and experiences. This can be achieved by incorporating stories, images, and examples that reflect the diversity of the target audience. By doing so, health messages become more relatable and culturally relevant.
In conclusion, cultural sensitivity and diversity are essential principles of health communication. Recognizing and respecting cultural differences, tailoring communication to meet diverse needs, and promoting inclusivity are key elements of effective health communication strategies. By embracing these principles, health communicators can ensure that their messages reach and resonate with diverse populations, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
Principle 3: Active Listening And Empathy
One of the fundamental principles of health communication is active listening and empathy. This principle emphasizes the importance of being present and attentive during interactions, listening without judgment or interruption, and showing compassion and understanding towards others. By practicing active listening and empathy, healthcare professionals and individuals can create a safe and supportive environment, improve patient satisfaction, and enhance the overall effectiveness of health communication.
Being present and attentive during interactions
Being present and attentive during interactions is crucial to effective health communication. It involves focusing on the speaker, maintaining eye contact, and eliminating distractions. By giving your undivided attention, you show respect and convey that the person’s thoughts and concerns are important. This level of attentiveness helps build trust and establishes a foundation for effective communication.
Listening without judgment or interruption
Listening without judgment or interruption is another essential aspect of active listening and empathy. It involves genuinely hearing what the speaker is saying without jumping to conclusions or forming biases. Rather than interjecting with personal opinions or solutions, strive to understand the speaker’s perspective fully. This shows respect and validates their experiences, creating a safe space where open and honest communication can thrive.
Showing compassion and understanding
A crucial component of active listening and empathy is showing compassion and understanding towards others. This involves recognizing and acknowledging their emotions, experiences, and concerns, even if they differ from your own. Demonstrating empathy lets the speaker feel heard and supported, fostering a stronger connection and facilitating more effective communication. By actively engaging with compassion and understanding, healthcare professionals can create a patient-centered approach that leads to better health outcomes.
In conclusion, active listening and empathy are essential principles of health communication that contribute to building strong relationships between healthcare providers and patients. By being present and attentive, listening without judgment or interruption, and showing compassion and understanding, individuals can create a supportive environment where effective communication thrives. Implementing these principles can lead to improved patient satisfaction, enhanced health outcomes, and a more empathetic and compassionate healthcare system.
Principle 4: Building Trust And Rapport
Establishing a trusting relationship with patients is a fundamental aspect of effective health communication. Trust forms the foundation of any successful healthcare interaction, as it fosters confidence, cooperation, and a sense of personal connection between the healthcare provider and the patient. Through the establishment of trust and rapport, healthcare professionals can better engage patients in their own health journey, leading to improved outcomes and overall satisfaction.
Establishing a Trusting Relationship with Patients
Building trust begins with creating a safe and supportive environment where patients feel comfortable expressing their concerns and sharing personal information. When patients feel heard and understood, they are more likely to trust the healthcare professional and actively participate in their own care. Here are some strategies healthcare providers can use to establish trust:
- Listen actively and attentively to patients, demonstrating empathy and respect for their perspectives.
- Take the time to answer questions and address any concerns or uncertainties the patient may have.
- Use clear and concise language to explain medical terms or procedures, avoiding jargon that may confuse or intimidate patients.
- Show genuine interest in the patient’s well-being and involve them in the decision-making process.
- Be responsive to patient needs and provide timely communication.
Being Transparent and Honest in Communication
Transparency and honesty in health communication are essential for building trust and ensuring patients have the necessary information to make informed decisions about their health. By being transparent and honest, healthcare providers can foster a sense of transparency that empowers patients to actively engage in their care. Here’s how healthcare professionals can practice transparency:
- Provide accurate and comprehensive information about the patient’s condition, diagnosis, and treatment options.
- Be honest about potential risks, benefits, and uncertainties associated with different interventions.
- Disclose conflicts of interest that may influence decision-making.
- Clearly communicate the limitations of medical knowledge and the evolving nature of healthcare practices.
Respecting Patient Autonomy and Preferences
Respecting patient autonomy and preferences is crucial for building trust and rapport in health communication. Recognizing that patients have the right to make decisions about their healthcare and respecting their choices helps establish a collaborative relationship based on mutual respect. To promote patient autonomy and preferences, healthcare providers should:
- Engage in shared decision-making, involving patients in discussions about treatment options and considering their values and goals.
- Respect patients’ right to refuse or seek alternative treatments.
- Listen to and validate patients’ concerns, preferences, and beliefs.
- Ensure confidentiality and privacy to foster trust and respect for the patient’s personal information.
By adhering to the principles of building trust and rapport, healthcare professionals can cultivate patient-centered care and enhance the effectiveness of health communication. A strong and trusting relationship with patients forms the basis for achieving positive health outcomes and ensuring patient satisfaction.
Principle 5: Utilizing Multiple Communication Channels
Principle 6: Health Literacy And Education
Health literacy refers to an individual’s ability to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services in order to make informed decisions about their own health. In principle 6 of health communication, health literacy and education play a crucial role in empowering individuals to take charge of their health and well-being. By assessing patient health literacy levels, providing education in a clear and engaging manner, and promoting self-management and informed decision-making, healthcare providers can ensure that patients are equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to make healthy choices.
Assessing patient health literacy levels
Assessing patient health literacy levels is an essential step in effective health communication. By understanding a patient’s level of health literacy, healthcare providers can tailor their communication strategies to ensure that information is delivered in a way that is easily understood. This can be done by using simple language, avoiding technical jargon, and utilizing visual aids such as diagrams or videos to enhance comprehension. Identifying any potential barriers to understanding can help healthcare providers address specific needs and provide the appropriate level of support.
Providing education in a clear and engaging manner
When it comes to health communication, it is crucial that information is presented in a clear and engaging manner. Healthcare providers should strive to explain complex medical concepts using simple and concise language. By breaking down information into easily digestible chunks, patients are more likely to understand and retain important health-related information. Utilizing visual aids, such as infographics or charts, can also enhance comprehension and engagement. Additionally, healthcare providers should encourage patients to ask questions and provide opportunities for clarification, ensuring that they feel well-informed and empowered in their decision-making process.
Promoting self-management and informed decision-making
Promoting self-management and informed decision-making is a key aspect of health literacy and education. Healthcare providers should empower patients to take an active role in managing their own health by providing them with the necessary knowledge and skills. This includes educating patients about the benefits of adopting healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, and the potential risks associated with certain lifestyle choices. By equipping patients with the information they need, healthcare providers can help individuals make informed decisions that are in line with their personal health goals.
In conclusion, Principle 6 of health communication highlights the importance of health literacy and education in empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health. By assessing patient health literacy levels, providing education in a clear and engaging manner, and promoting self-management and informed decision-making, healthcare providers can contribute to the overall well-being of their patients.
Principle 7: Feedback And Continuous Improvement
Feedback and continuous improvement are integral aspects of effective health communication. Seeking feedback from patients and healthcare providers, incorporating this feedback for ongoing improvement, and implementing strategies to enhance communication effectiveness are all essential for ensuring quality healthcare delivery.
Seeking feedback from patients and healthcare providers
One of the key principles of health communication is actively seeking feedback from both patients and healthcare providers. This feedback provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of communication strategies and helps identify areas for improvement. Patient feedback enables healthcare providers to understand the patient’s perspective, address any concerns or misunderstandings, and deliver care that aligns with the patient’s needs and preferences.
Feedback from healthcare providers allows a comprehensive understanding of the challenges they face in communicating with patients, and the information gaps that can hinder effective healthcare delivery. By actively seeking feedback from patients and healthcare providers, healthcare organizations can gain a holistic view of their communication practices and work towards creating an environment that promotes open dialogue and effective information exchange.
Incorporating feedback for ongoing improvement
While seeking feedback is an important step, incorporating this feedback into ongoing improvement efforts is equally vital. Healthcare organizations should establish mechanisms to collect and analyze feedback systematically. This analysis can help identify recurring trends, areas requiring improvement, and potential solutions.
Implementing changes based on the feedback received can lead to better patient outcomes, increased patient satisfaction, and improved overall communication effectiveness. This ongoing improvement process ensures that healthcare providers consistently integrate patient and provider feedback to enhance their communication strategies and deliver quality care.
Implementing strategies to enhance communication effectiveness
Feedback alone is not enough; healthcare organizations must also implement strategies to enhance communication effectiveness. These strategies may include developing and providing training programs for healthcare providers to improve their communication skills, adopting new technologies to facilitate efficient information exchange, and ensuring clear and accessible communication materials for patients.
By actively investing in strategies to enhance communication effectiveness, healthcare organizations can minimize communication barriers, improve patient-provider relationships, and ultimately deliver better healthcare outcomes. Regularly assessing and updating these strategies ensures that healthcare providers stay current with the evolving communication needs and preferences of patients and have the tools and knowledge to effectively engage in health communication.
In conclusion, feedback and continuous improvement play a crucial role in health communication. Seeking feedback from patients and healthcare providers, incorporating this feedback for ongoing improvement, and implementing strategies to enhance communication effectiveness are fundamental principles that drive positive healthcare outcomes. By embracing these principles, healthcare organizations can foster a culture of effective and patient-centered communication, leading to improved healthcare experiences for all involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The 5 Principles Of Communication?
The 5 principles of communication are clarity, conciseness, correctness, completeness, and consideration.
What Is The 7 Principles Of Communication?
The 7 principles of communication are guidelines for effective communication. They include clarity, brevity, consistency, sincerity, context, listening, and feedback. These principles help ensure messages are clear, concise, honest, and considerate of the audience.
What Are The Key Principles Of Effective Communication In Healthcare?
The key principles of effective communication in healthcare are brevity, clarity, active voice, and SEO friendliness. By keeping sentences short and using active voice, communication in healthcare can be easily understood and optimized for search engines.
What Are The 5 Elements Of Communication In Healthcare?
The 5 elements of communication in healthcare are: verbal communication, non-verbal communication, active listening, clarity, and empathy.
Conclusion
Effective health communication is crucial for promoting healthy behaviors and improving public health outcomes. By applying the principles of health communication, we can ensure that information is delivered in a clear, concise, and accessible manner. Firstly, using plain language and avoiding jargon helps to make health messages easily understandable to a wide audience.
Secondly, tailoring health messages to the specific needs, values, and beliefs of the target population enhances their relevance and receptivity. Thirdly, utilizing multiple channels of communication, such as social media, websites, and community forums, increases the reach and impact of health messages.
Fourthly, fostering interactive and two-way communication, such as through discussion forums or feedback mechanisms, encourages audience engagement and participation. Lastly, incorporating visuals, such as infographics or videos, can enhance comprehension and retention of health information. By adhering to these principles, health communicators can effectively convey information, facilitate behavior change, and ultimately improve the overall health of individuals and communities.